Understanding the Thyroid Gland and Its Functions
The thyroid gland is a small, butterfly-shaped organ located at the base of our neck, just below the Adam's apple. This vital gland plays a crucial role in our body by producing and releasing two essential hormones: thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3). These hormones are responsible for regulating our body's metabolism, growth, development, and overall energy levels.
When our thyroid gland functions properly, it maintains a delicate balance of hormones to ensure that our body's metabolism is running smoothly. However, certain factors can disrupt this balance, leading to thyroid disorders such as hypothyroidism (underactive thyroid) or hyperthyroidism (overactive thyroid). In this article, we will focus on the role of carbimazole in managing thyroid health, particularly in cases of hyperthyroidism.
Hyperthyroidism: Symptoms and Causes
Hyperthyroidism is a condition characterized by the overproduction of thyroid hormones, which can lead to various symptoms such as weight loss, increased heart rate, irritability, anxiety, tremors, and difficulty sleeping. This condition can be caused by various factors, including the autoimmune disorder Graves' disease, inflammation of the thyroid gland (thyroiditis), and the overconsumption of iodine.
Diagnosing hyperthyroidism typically involves a series of blood tests to measure the levels of thyroid hormones and thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) in the body. If left untreated, hyperthyroidism can lead to severe complications, such as heart problems, bone loss, and even a potentially life-threatening condition called thyroid storm.
Carbimazole: An Overview and Its Mechanism of Action
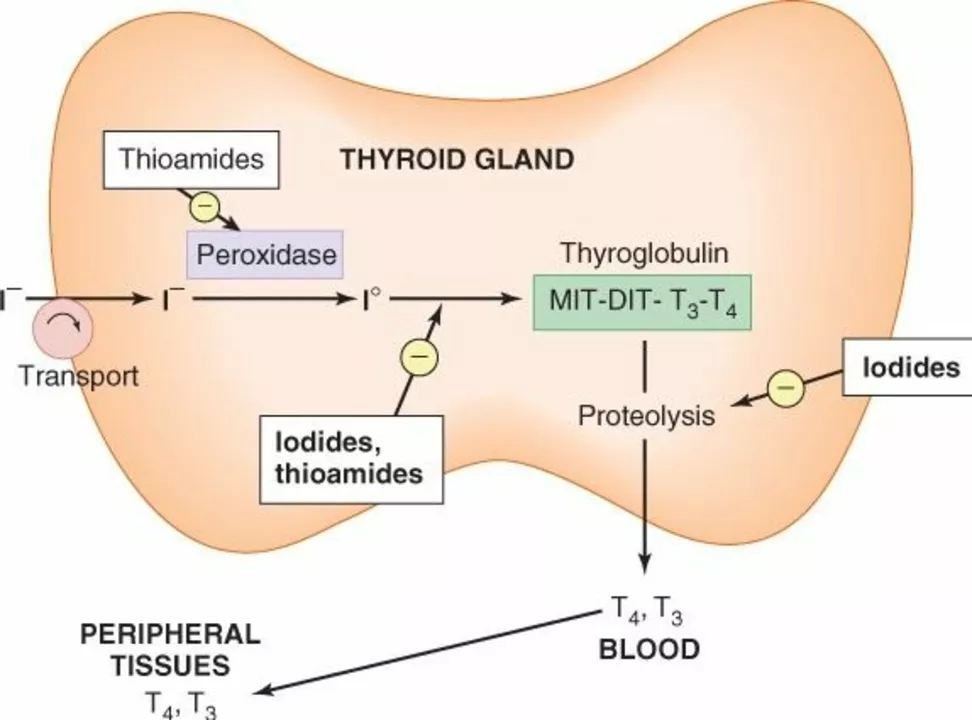
Carbimazole is an antithyroid medication commonly prescribed to treat hyperthyroidism. It belongs to a class of drugs called thionamides, which also includes methimazole and propylthiouracil (PTU). Carbimazole works by inhibiting the production of thyroid hormones in the thyroid gland, thereby helping to restore a normal hormonal balance in the body.
More specifically, carbimazole acts by blocking the enzyme called thyroid peroxidase, which is responsible for the synthesis of T4 and T3 hormones. By inhibiting this enzyme, carbimazole effectively reduces the excessive production of thyroid hormones and alleviates the symptoms associated with hyperthyroidism.
Dosage and Duration of Carbimazole Treatment
The dosage and duration of carbimazole treatment may vary depending on the severity of the hyperthyroidism and the patient's individual response to the medication. Typically, a doctor will start with a higher dose to quickly bring the hormone levels under control and then gradually decrease the dose as the thyroid function normalizes.
It is crucial to follow your doctor's instructions when taking carbimazole and to have regular blood tests to monitor your thyroid hormone levels. The duration of treatment may range from a few months to more than a year, depending on the underlying cause of hyperthyroidism and the patient's response to the medication.
Side Effects and Precautions While Taking Carbimazole
As with any medication, there are potential side effects associated with carbimazole. Some common side effects include headache, nausea, upset stomach, and skin rash. These side effects are generally mild and tend to subside as the body adjusts to the medication. However, if you experience any persistent or severe side effects, it is essential to consult your doctor immediately.
Rare but serious side effects of carbimazole include a severe decrease in white blood cells (agranulocytosis) and liver problems. If you develop symptoms such as fever, sore throat, or yellowing of the skin and eyes (jaundice), seek medical attention right away. It is also important to inform your doctor of any other medications or supplements you are taking, as certain drugs may interact with carbimazole.
Carbimazole and Pregnancy: Risks and Considerations
Carbimazole can be harmful to an unborn baby, especially during the first trimester of pregnancy. If you are pregnant or planning to become pregnant, it is crucial to discuss your treatment options with your doctor. In some cases, your doctor may recommend switching to another antithyroid medication, such as propylthiouracil (PTU), which is considered safer during pregnancy.
It is also important to note that breastfeeding while taking carbimazole is generally not recommended, as the medication can pass into breast milk and potentially affect the baby's thyroid function. If you are breastfeeding or planning to breastfeed, discuss your options with your healthcare provider to ensure the safety and well-being of both you and your baby.

Wow, reading about carbimazole feels like watching a dramatic rescue scene inside our own bodies! The way it tames an overactive thyroid is nothing short of heroic, gently guiding those wild hormones back into balance. Remember, staying patient with dosage adjustments can make the journey smoother, and your doctor’s guidance is the best compass.
For anyone starting carbimazole, it helps to think of the dosage schedule as a graduated plan. Begin with the initial dose prescribed, then allow your endocrinologist to taper it based on regular TSH and free T4 readings. Consistency with blood tests every 4‑6 weeks ensures you’re neither under‑ nor over‑treated, and keeping a medication log can simplify discussions during appointments.
Carbimazole just blocks thyroid hormone production, plain and simple.
Adhering to the prescribed regimen is paramount for optimal outcomes 😊. Regular monitoring not only confirms therapeutic efficacy but also safeguards against rare adverse events such as agranulocytosis. Should you notice any signs of infection or unusual fatigue, prompt medical consultation is essential.
People often think they can self‑medicate or skip appointments but that mindset is dangerous ignoring a doctor's advice on carbimazole dosage can lead to severe complications like heart issues or bone loss it's a responsibility to follow medical guidance and respect the seriousness of hormone regulation
The pharmacodynamic profile of carbimazole involves irreversible inhibition of thyroid peroxidase, thereby attenuating organification of iodide and coupling of iodotyrosines-a mechanistic cascade crucial for curbing T3/T4 synthesis. Clinically, this translates to a dose‑dependent suppression of serum thyroxine, necessitating titration based on bio‑chemical feedback loops. Moreover, awareness of its bioavailability and hepatic metabolism informs potential drug‑drug interactions, especially with agents that are CYP450 substrates.
Carbimazole remains one of the cornerstone antithyroid agents due to its predictable pharmacokinetics and relatively favorable safety profile compared with alternatives.
Upon oral administration, it is rapidly converted to its active metabolite methimazole, which exerts the therapeutic effect.
The inhibition of thyroid peroxidase by methimazole reduces the iodination of tyrosine residues on thyroglobulin, effectively diminishing the synthesis of both T4 and T3.
Clinicians typically initiate therapy at a dose ranging from 15 to 40 mg per day, adjusted according to the severity of hyperthyroidism and the patient's baseline hormone levels.
Regular monitoring of serum TSH, free T4, and free T3 should be performed every four to six weeks during the titration phase.
This ensures that overtreatment, which could precipitate iatrogenic hypothyroidism, is avoided.
In addition to routine blood work, patients should be educated about the warning signs of agranulocytosis, such as sudden fever, sore throat, or oral ulcerations.
Should any of these symptoms arise, immediate discontinuation of carbimazole and urgent medical evaluation are mandatory.
For pregnant individuals, the risk–benefit assessment becomes more nuanced; methimazole exposure in the first trimester has been associated with specific congenital anomalies, prompting some clinicians to preferentially prescribe propylthiouracil during early gestation.
However, propylthiouracil carries its own risk of hepatotoxicity, necessitating careful hepatic function monitoring.
Long‑term remission can be achieved in a subset of patients through definitive therapies such as radioactive iodine ablation or thyroidectomy, after which carbimazole is typically tapered off.
Nonetheless, for many patients, especially those with mild disease or contraindications to definitive treatment, a prolonged course of carbimazole remains the most practical approach.
Lifestyle considerations, including adequate iodine intake and avoidance of excessive thyroid‑stimulating substances, can augment pharmacological therapy.
Dietary supplementation with selenium has shown modest benefits in reducing oxidative stress within the thyroid gland, though it should not replace standard treatment.
Ultimately, individualized dosing guided by serial thyroid function tests, patient tolerance, and clinical judgment provides the best pathway to disease control.
Open communication between the patient and endocrinology team is essential to navigate dosage adjustments, side‑effect management, and long‑term planning.