Carbimazole — what it is and why doctors prescribe it
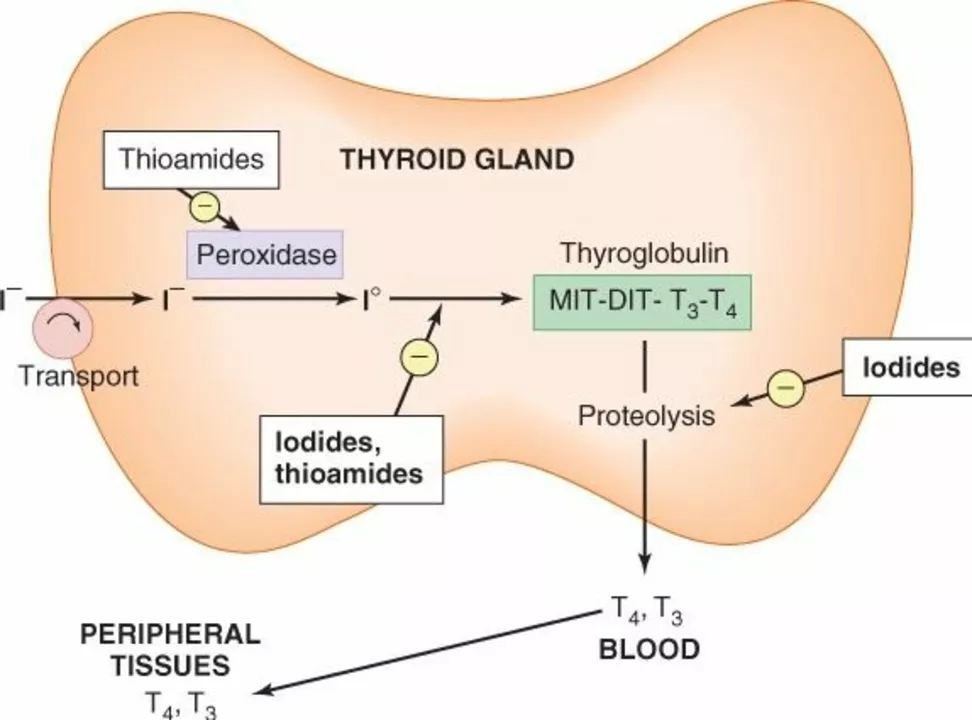
Carbimazole is a common antithyroid medicine used to treat hyperthyroidism (an overactive thyroid). It works by blocking the thyroid gland’s ability to make thyroid hormones. In the body carbimazole quickly converts to methimazole, the active form that reduces T3 and T4 production and helps symptoms like fast heartbeat, tremor, and heat intolerance settle down.
How people typically take carbimazole
Doctors choose a starting dose based on how overactive the thyroid is. Typical adult starting doses range from about 15–40 mg per day, often split into one or two doses. Once symptoms and blood tests improve, the dose is lowered to a maintenance level—often 5–15 mg daily. Kids get lower doses based on weight. These numbers are only examples; follow your doctor’s plan.
Carbimazole is usually taken with food to reduce stomach upset. Some clinics give a single daily dose because the active drug lasts a while; others split the dose. Always follow instructions from your prescriber or pharmacist.
Side effects, risks, and what to watch for
Most people have mild side effects like rash, itchiness, nausea, or joint aches. Two important but rare problems need quick action: agranulocytosis and liver injury. Agranulocytosis means very low white blood cells and shows up as sudden fever, sore throat, mouth ulcers, or unusual infections. If that happens, stop the drug and get urgent medical care. Liver problems can cause yellowing of the skin, dark urine, or severe stomach pain—seek prompt help for those signs too.
Because these risks are serious, doctors often check blood counts and liver tests before starting carbimazole and repeat tests during the first few months of treatment. Thyroid blood tests (TSH, free T4) are used to track effectiveness and adjust dose.
Pregnancy and breastfeeding: carbimazole can cause rare birth defects early in pregnancy. Many guidelines prefer propylthiouracil (PTU) in the first trimester and switching to carbimazole or methimazole later. If you are pregnant, planning pregnancy, or breastfeeding, discuss this with your doctor—do not stop medicines on your own.
Drug interactions: carbimazole can affect warfarin dosing and may interact with other drugs that affect blood counts or liver function. Tell your provider about all medications, supplements, and herbal products you use.
Practical tips: keep a list of symptoms to report (fever, sore throat, yellow skin), carry an alert that you take an antithyroid drug, and keep regular blood tests as advised. If you miss a dose, follow your doctor or pharmacist’s advice—don’t double up without checking.
Carbimazole is effective but not risk-free. Clear communication with your doctor, timely blood tests, and watching for warning signs make treatment much safer. If you have questions about dosing, pregnancy, or side effects, contact your healthcare team—fast.